A few days ago, we bid farewell to 2023; a year that witnessed numerous achievements in the medical field. In this article, we share some of these achievements.
Transplanting a Thawed Kidney
Researchers from the University of Minnesota managed to transplant thawed kidneys in rats. The team started by removing the kidneys of five rats and freezing them; after that, they successfully transplanted the frozen kidneys after letting them thaw to restart their biological clocks. This is an unprecedented achievement in the field of organ transplantation. If this technique proves successful in humans, it will mark a breakthrough that would save thousands of lives.
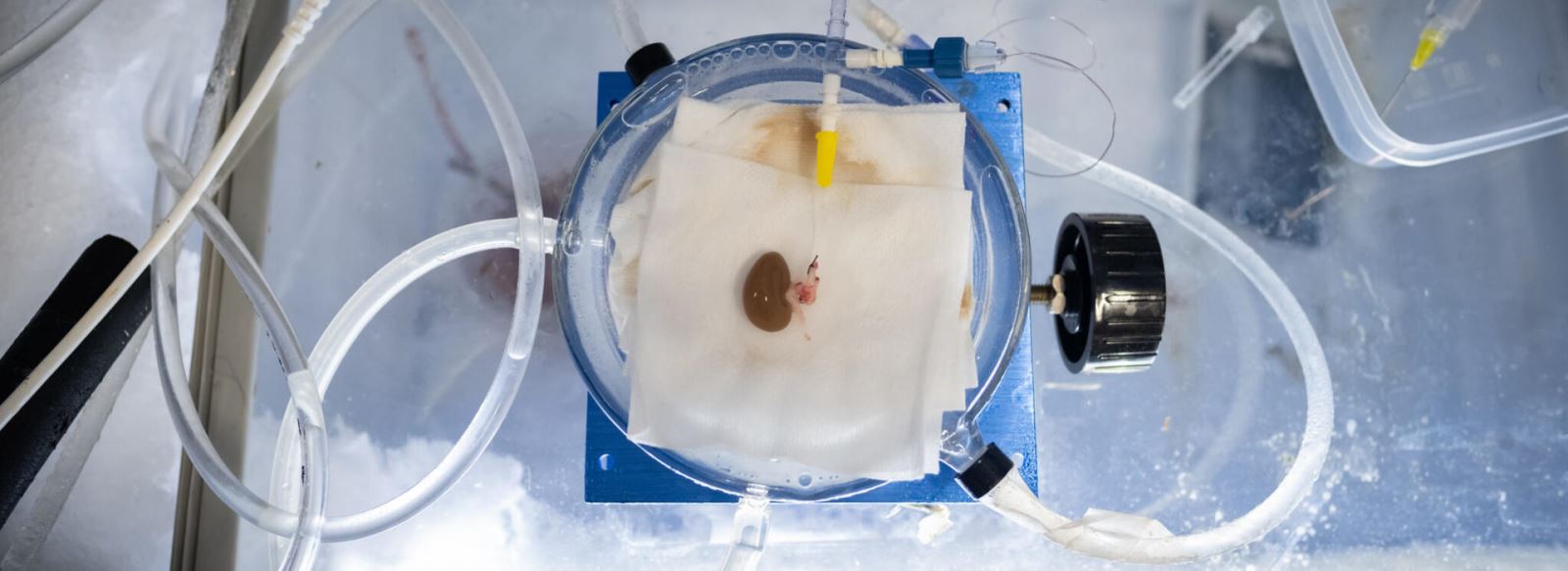 Source: med.umn.edu
Source: med.umn.edu
Obesity Drug with Other Health Benefits
In August 2023, Novo Nordisk Pharmaceutical Company published the results of a clinical trial that involved about 17,000 people. The results showed that patients suffering from obesity and cardiovascular diseases who take Semaglutide medicine are 20% less exposed to the risk of developing heart attacks than those who do not take it. This was the first large-scale study to prove that the medication had health benefits other than weight loss. Distinguished Science periodical described these findings as the achievement of 2023.
Semaglutide belongs to a class of medications known as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). It mimics the GLP-1 hormone, which promotes the production of insulin and demotes the production of glucagon, to reduce blood sugar. These medications were originally developed for diabetes, but clinical trials have proven their effectiveness in safe weight loss.
New Medication for Alzheimer's
According to reports of three clinical studies published in July 2023, a new medication for Alzheimer's disease has achieved promising results. While the available drugs are concerned with the symptoms only, this new medication targets the disease itself by targeting the amyloid protein to slow down cognitive deterioration. The accumulation of this protein is toxic to neurons, which disturbs communication among brain cells. Although the medication's effectiveness has been proven, some patients might witness side effects, including brain hemorrhage and swelling. Nevertheless, it is still considered a step forward on the road to developing a medication for Alzheimer's disease.
Translating Brain Ideas
A team at the University of Texas managed to translate ideas inside the human brain into a written text, using the Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (FMRI) device. This was made possible through developing a dictionary for the activity that takes place inside the brain when the person listens to words or watch images. The brain activity is deciphered through the use of AI algorithms and then converted into written texts.
This promising medical achievement is still in its very early stages. It still cannot be done outside the research laboratory and requires the person to spend about 15 hours inside the FMRI device to train the AI model. Yet, it represents hope to patients who are incapable of speech, such as those with strokes. Researchers say that future updates would use a portable device instead of the FMRI.
 Image by kjpargeter on Freepik
Image by kjpargeter on Freepik
References
quantamagazine.org
science.org
science.org
nationalgeographic.com
healthitanalytics.com
Cover image by KamranAydinov on Freepik.