| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35 |36 |review |
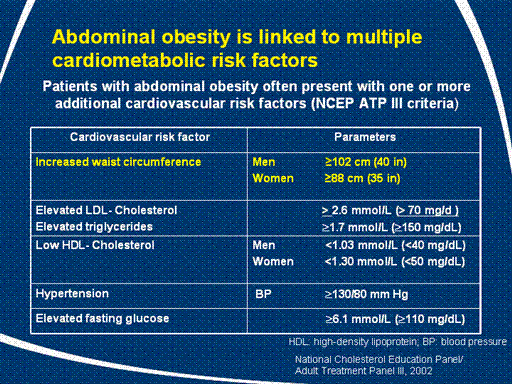 |
Abdominal obesity is linked to multiple cardiometabolic
risk factors
Abdominal obesity is associated with multiple cardiometabolic
risk factors, including
dyslipidaemia, elevated blood glucose, type 2 diabetes and inflammation
– all factors leading to the development of cardiovascular disease and
diabetes (Després JP et al, 1990; Pouliot MC, 1992; Kissebah AH
et al, 1989; Carey VJ, 1997; Turkoglu C et al, 2003).
Analysis of data from the NHANES 1999–2000 cohort from the USA
shows that high waist
circumference (NCEP/ATP III definition) is commonly associated with
other cardiometabolic risk factors. Overall, 86% of abdominally obese
patients had at least one other cardiometabolic risk factor (NHANES data on file).
|