Gender of nouns
Egyptian nouns distinguish two genders: masculine and feminine.
a) Masculine nouns are either substantive or derivative nouns:
i) Substantive nouns are words typically used to refer to people, objects, living organisms and the like.
ii) Derivative nouns are those words derived from verbs, infinitive, participle, and adjective.
|
To follow
|
Sms
|
𓌞𓋴𓂻
|
Follower
|
Smsw
|
𓌞𓋴𓍢𓂻𓀀
|
|
To say
|
Dd
|
𓆓𓂧
|
Speaker
|
Dddy
|
𓆓𓂧𓂧𓏭
|
|
To be great
|
wr
|
𓅨𓂋
|
Great
|
wr (w)
|
𓅨𓂋𓀀
|
b) Feminine nouns are also either substantive or derivative nouns and they almost always end in t
Substantive nouns
|
horizon
|
Axt
|
𓈌𓏏𓏤
|
|
woman
|
st
|
𓊃𓏏𓁐
|
Derivative nouns
|
To beautify
|
nfr
|
𓄤𓆑𓂋
|
Beautiful (f.)
|
nfrt
|
𓄤𓆑𓂋𓏏𓁐
|
Some nouns end with 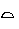 but they are not feminine, as the
but they are not feminine, as the tis part of the stem or the construction of the word.
tis part of the stem or the construction of the word.
|
statue
|
twt
|
𓏏𓅱𓏏𓀾
|
|
tree
|
xt
|
𓆱𓏏𓏤
|
In most cases the feminine noun is by adding the to the masculine noun, and change the determinative.
to the masculine noun, and change the determinative.
|
Daughter
|
sAt
|
𓅭𓏏𓁐
|
Son
|
sA
|
𓅭𓏤𓀀
|
|
Goddess
|
nTrt
|
𓊹𓂋𓏏𓆗
|
God
|
nTr
|
𓊹𓏤
|
|
Sister
|
snt
|
𓌢𓈖𓏏𓁐
|
Brother
|
sn
|
𓌢𓈖𓀀
|