| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |review |
 |
Background: Despite improved SVR
associated with PEG IFN monotherapy, relapse rates following treatment
discontinuation remain high and most patients with HCV genotype 1 do not
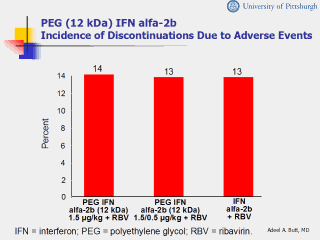
achieve SVR. Objective: To assess the efficacy and safety of PEG IFN alfa-2b plus RBV and identify predictors of response. Methods: Adults with HCV who had undergone liver biopsy within 1 year and had serum ALT greater than the upper limit of normal were randomized to receive SC PEG IFN alfa-2b 1.5 μg/kg QW plus oral RBV 800 mg for weeks; SC PEG IFN alfa-2b 1.5 μg/kg QW for 4 weeks followed by 0.5 μg/kg QW for the next 44 weeks plus oral RBV 1000-1200 mg/d for 48 weeks; or SC IFN alfa-2b 3 MIU TID plus oral RBV 1000-1200 mg/d for 48 weeks. Results: Data from 1530 subjects were included in the ITT analysis. Baseline characteristics were similar among the 3 groups and to those in previous reports. A high proportion of subjects in both PEG IFN alfa-2b groups achieved SVR. Of particular interest, 42% of subjects in the higher-dose PEG IFN alfa-2b group with HCV genotype 1 achieved SVR; yet no apparent benefit was observed in subjects in either PEG IFN alfa-2b group with genotypes 2 or 3. Further, while subjects with lower viral load (<2 X 106/mL) responded better to PEG IFN alfa-2b plus RBV therapy, those with high viral levels did not (42%, 42%, and 42%, respectively for higher-dose PEG IFN alfa-2b, lower-dose PEG IFN alfa-2b, and IFN alfa-2b). Logistic regression analysis identified PEG IFN alfa-2b and RBV doses as predictors of SVR, with higher doses of RBV given in combination with higher-dose PEG IFN alfa-2b increasing the likelihood of SVR. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that baseline viral load and HCV genotype were independent predictors of response, as were age and the presence of bridging fibrosis/cirrhosis (PegIntron). The safety of PEG IFN alfa-2b plus RBV was similar to that of IFN alfa-2b plus RBV. Conclusion: Of the 3 regimens, PEG IFN alfa-2b 1.5 μg/kg QW plus RBV is the most effective, with subjects with HCV genotype 1 benefiting the most. References Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, et al, for the International Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with IFN alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001;358:958-965. PegIntron [package insert]. Kenilworth, NJ: Schering Corporation; 2001. |