Today, the internet has revolutionized the way we access information. With a few keywords typed on popular search engines, numerous results appear within seconds, from various pages with close answers to our questions. This process falls within the scope of the "surface web", which includes websites and webpages publicly accessible through search engines, or by directly typing the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) into a web browser.
If we compare the internet to an iceberg, the surface web represents its visible part, which constitutes 4% only, and includes websites with domain names that follow popular domain extensions—for example, .com, .net, or .org. The larger part of the iceberg, representing 90% of the internet, is the "deep web", which can be considered the hidden part of the iceberg. The deep web includes private databases, such as inboxes, governmental documents, and any content that requires a login, as these pages are not indexed by a search engine.
There is also a deeper part, which is the "dark web"; it is part of the deep web that is intentionally hidden and cannot be accessed using traditional methods. It constitutes 6% of the internet and features anonymous browsing and data encryption. The dark web is a digital underworld, infamous for its prohibited content and illegal activities, such as fraud, drug, and firearm trafficking. Yet, it encompasses legal activities, such as unrestricted, secure private communication. Both the deep web and the dark web are hidden from standard search engines. Accessing the deep web requires a specific web address, while the dark web needs specialized applications, browsers, and knowledge.
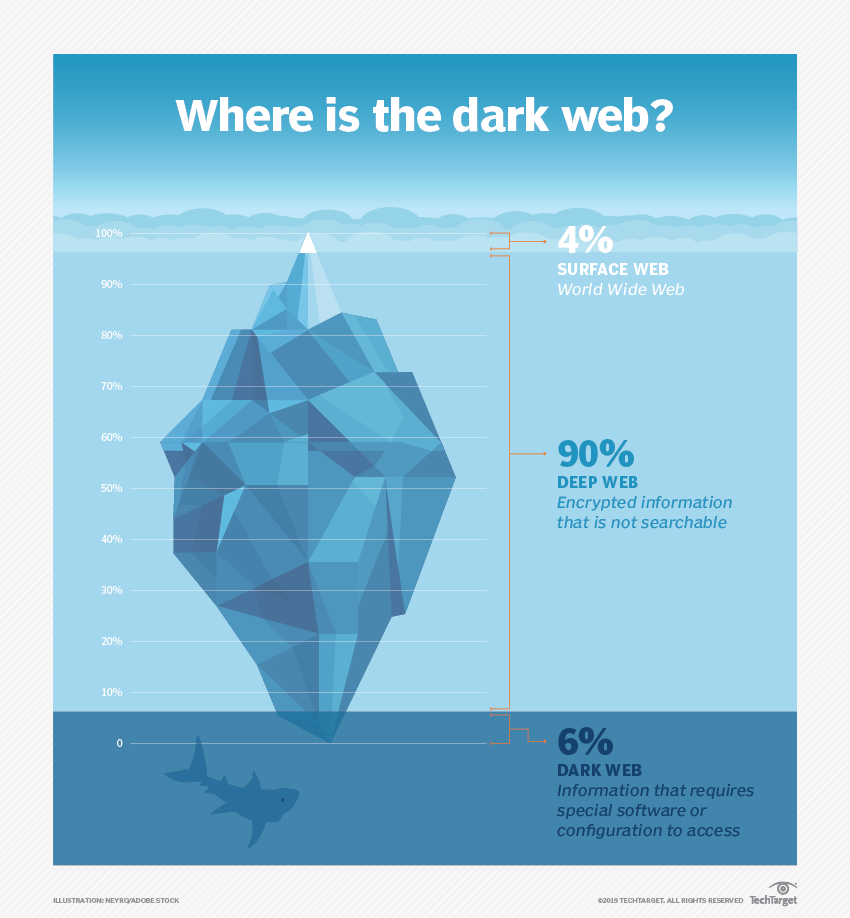 Image source: www.techtarget.com
Image source: www.techtarget.com
The dark web emerged in 2000, when the Scottish student Ian Clarke launched his university project "Freenet" that shall enable users to communicate and share their files online anonymously. This Project is the foundation of the "Tor" project (short for "The Onion Router"), initiated in 2002. It leverages layered encryption, mimicking the layered structure of an onion, to enable anonymous internet browsing.
Another illicit activity on the dark web involves buying and selling passwords. Suspicious websites are subject to closure by government authorities, as demonstrated by the shutdowns of the Silk Road, AlphaBay, and Hansa markets. Nevertheless, dark web users remain vulnerable to security breaches and data leaks.
The internet we commonly access is known as the surface web. Hidden beneath the surface lie the worlds of the deep web and dark web. The dark web is primarily known for the prevalence of illicit activities, despite its potential for legitimate uses, such as privacy and secure communications. Its risks include exposure to malicious software and data breaches. You have now learned about the web and explored its hidden depths.
References
https://www.for9a.com/learn/ماذا-تعرف-عن-الإنترنت-المظلم-والإنترنت-العميق
https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/dark-web
https://sopa.tulane.edu/blog/everything-you-should-know-about-dark-web
Cover designed by Freepik